
- Inr normal range with acute stroke Activator#
- Inr normal range with acute stroke portable#
- Inr normal range with acute stroke professional#
In addition to demographic information, admission INR, and indication for warfarin therapy baseline laboratory results, stroke characteristics when applicable (Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment criteria), thrombolytic administration, and outcome (discharge modified Rankin scale score ) data were collected. They were categorized by final diagnosis using history, examination, laboratory data, and neuroimaging (MRI and non-contrast head CT) into ischemic (ischemic stroke or TIA) versus non-ischemic (hemorrhagic stroke or stroke mimic ). Patients were evaluated by a neurologist as part of the “brain attack (BAT)” or acute stroke code. Patients were excluded if they failed to meet the above criteria, had lack of further follow-up information regarding diagnosis, or were on warfarin because of mechanical valve (different INR goal: 2.5–3.5). This registry is maintained by our Stroke Program to track patients presenting to the Emergency Department with symptoms concerning for acute stroke. Eligible patients included adults (age ≥18 years), with warfarin documented as home medication, who had an INR obtained at presentation, and were included in our Brain Attack Registry. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Johns Hopkins Health System. The aim of the present study is to determine the likelihood of ischemia (stroke or transient ischemic attack ) in patients on warfarin who present with stroke-like symptoms, based on their INR result.Ī retrospective analysis was performed of all patients presenting to our urban, academic stroke center with symptoms suggestive of acute stroke within the last 6 h, who were also on warfarin, between January 1, 2013, and December 31, 2014. For many indications, such as atrial fibrillation or a hypercoagulable state, a sub-therapeutic INR could increase risk for an ischemic stroke. Unfortunately, patients are often sub-therapeutic given the difficulty in controlling INR due to medication and food interactions. For the majority of patients on warfarin, available guidelines recommend an INR goal of 2–3. There is little published data regarding the incidence of ischemic stroke in patients already on warfarin with varying INR cutoffs, or the predictive value of INR in informing the likelihood of ischemia versus a stroke mimic. Another reason to obtain an INR on admission in these patients may be its ability to help determine the likelihood of ischemia.


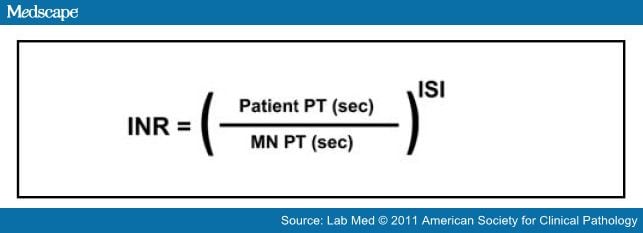
Because of this, tests of coagulation are included in the acute workup of patients on anticoagulation who present with new neurologic deficits. The use of warfarin by itself is not an absolute contraindication to rt-PA administration though due to increased bleeding risk, an international normalized ratio (INR) of >1.7 is a contraindication.
Inr normal range with acute stroke Activator#
Rapid assessment of patient eligibility for intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) is critical in these cases to re-establish blood flow to the ischemic area. Nearly 90% of all stroke cases are ischemic in nature. However, as concordance with laboratory INR values decreases with higher INR values, it is recommended that with CoaguChek S INRs in the > 1.5 range, a standard laboratory measurement be used to confirm the results.Stroke is the fifth leading cause of mortality in the United States.
Inr normal range with acute stroke professional#
When used by a trained health professional in the emergency department to assess INR in acute ischemic stroke patients, the CoaguChek S is reliable and provides rapid results. In the AIS group alone, the correlation coefficient and 95% CI was also high 0.937 (0.59 - 0.74) and diagnostic accuracy of the POCT device was 94%. The interclass correlation coefficient and 95% confidence interval between overall POCT device and standard laboratory value INRs was high (0.932 (0.69 - 0.78). The INR's were measured using the Roche Coaguchek S and the standard laboratory technique. The objective of this study was to evaluate the reliability, validity, and impact on clinical decision-making of a POCT device for INR testing in the setting of acute ischemic stroke (AIS).Ī total of 150 patients (50 healthy volunteers, 51 anticoagulated patients, 49 AIS patients) were assessed in a tertiary care facility.
Inr normal range with acute stroke portable#
In the emergency department, portable point-of-care testing (POCT) coagulation devices may facilitate stroke patient care by providing rapid International Normalized Ratio (INR) measurement.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
